
Published: Jan 8, 2026 by R. Vleeshouwers

Published: Jan 8, 2026 by R. Vleeshouwers
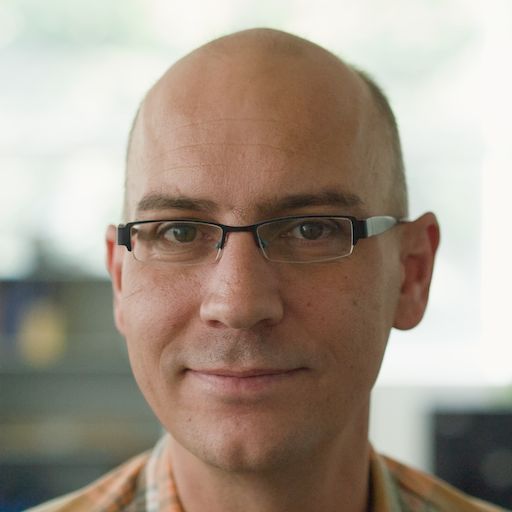
This tutorial will guide you through the process of transforming a regular photograph into a vibrant, comic-book-style pop art image using the powerful ComfyUI interface. The workflow demonstrated is a “context” or “style transfer” setup, where an existing image (the reference) provides the artistic style for a new image (the subject).
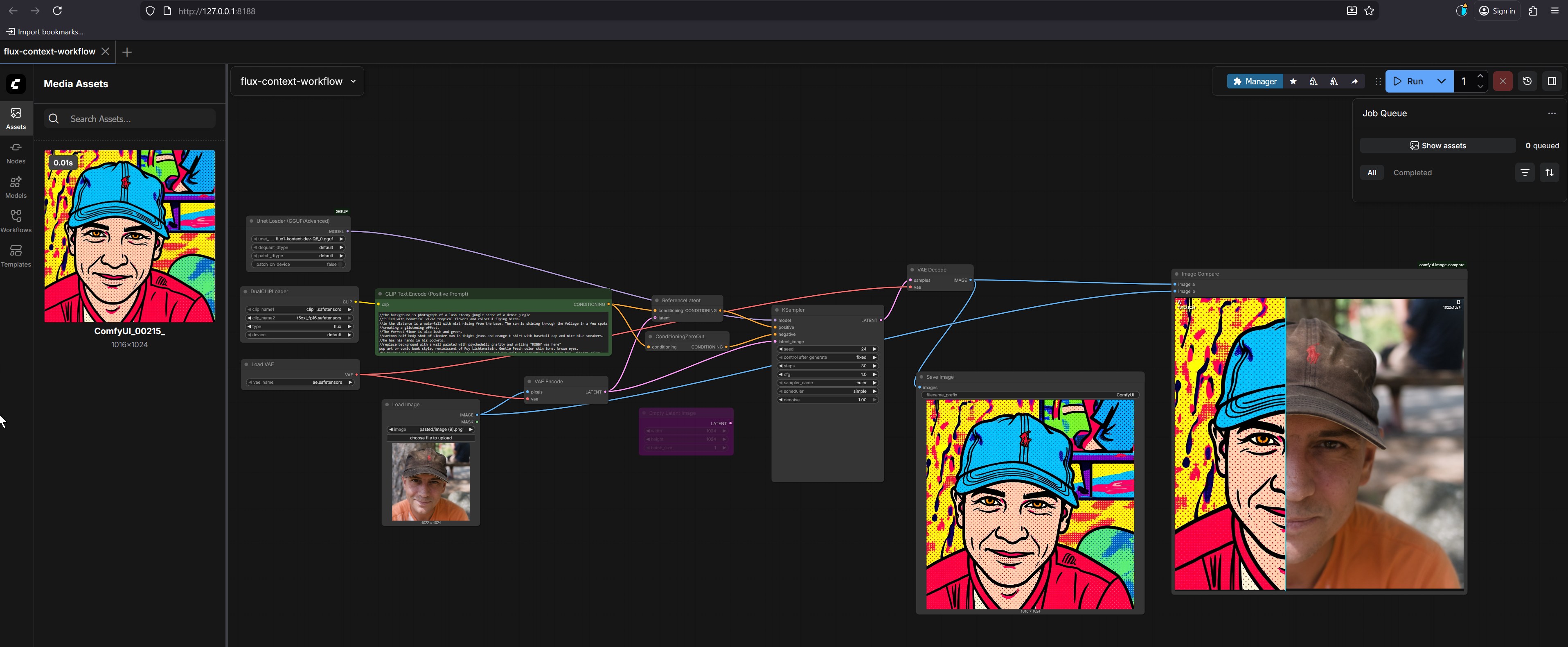
The final result, visible in the Image Compare and Save Image nodes, is a split-screen image:
Our goal is to replicate the artistic style from the reference image (the pop art portrait) onto the subject image (the photo).
ComfyUI is a powerful, node-based interface for Stable Diffusion models. Here’s how to get it set up on your computer.
Open a terminal (or command prompt) and run the following commands:
# Clone the ComfyUI repository from GitHub
git clone https://github.com/comfyanonymous/ComfyUI.git
# Navigate into the ComfyUI directory
cd ComfyUI
You will need to install the required Python packages. The easiest way is to use pip.
# Install the required packages
pip install -r requirements.txt
ComfyUI needs several models to function. You must download them manually.
.safetensors or .ckpt). The most common one is flux-1-dev-fp8.safetensors.models/checkpoints folder within your ComfyUI directory.vae-ft-mse-840000-ema-pruned.safetensors.models/vae folder within your ComfyUI directory.Run the following command to start ComfyUI:
# Start ComfyUI
python main.py --listen 127.0.0.1:8188 --listen-port 8188
http://127.0.0.1:8188.Open a web browser and go to http://127.0.0.1:8188. You should see the ComfyUI interface.
Let’s walk through the entire process with a specific example.
http://127.0.0.1:8188.Workflows tab in the left sidebar.flux-context-workflow to load it into the main graph.The reference image is the source of the artistic style. In this case, it’s the pop art portrait.
Media Assets panel on the left, locate the image named ComfyUI_00215_. This is your reference image.Media Assets panel into the main graph area. It should automatically connect to the Unet Loader node.The subject image is the one you want to transform.
Media Assets panel, find the photo of the man wearing a brown cap.Load Image node.The text prompt describes the desired content and style. The prompt is already provided in the CLIP Text Encode (Positive Prompt) node.
CLIP Text Encode (Positive Prompt) node to edit the text./the background is a photograph of a lush steamy jungle scene of a dense jungle
//filled with beautiful vivid tropical flowers and colorful flying birds.
//as the distance is a waterfall with mist rising from the base. The sun is shining through the foliage in a few spots
//creating a glittering effect.
//The reference image is also lush and green,
///a cartoon half body shot of slender man in tight jeans and orange t-shirt with baseball cap and nice blue sneakers.
//He has his hands in his pockets.
//Replace background with a wall painted with psychedelic graffiti and writing "KERRY was here"
//pop art or comic book style, reminiscent of Roy Lichtenstein. Gentle Peach color skin tone, brown eyes.
Run button in the top-right corner of the ComfyUI interface.flux-context-dev-Q8.gguf) is loaded.Save Image node.Image Compare window, where it is displayed side-by-side with the original photo for comparison.The power of ComfyUI lies in its modular node-based system. Each node performs a specific function, and they are connected to form a complete workflow. Let’s break down the key nodes in this flux-context-workflow.
Unet Loader (GGUF/Advanced)flux-context-dev-Q8.gguf) into memory. The model is responsible for generating the final image based on all the inputs.Load ImageCLIP Text Encode (Positive Prompt)VAE EncodeKSamplersteps (how many times the AI refines the image) and cfg (how closely the image follows the prompt) to control the quality.VAE DecodeVAE Encode node. It takes the generated latent image from the KSampler and converts it back into a standard image format.Save ImageThe prompt is the most powerful tool for controlling the final output. By changing the words and phrases, you can create images in countless different styles.
The prompt in the image uses a specific syntax:
/the background is...: This is a negative prompt. It tells the AI what not to include.//The reference image is also lush and green,: This is a contextual hint. It instructs the model to apply the style of the reference image.///a cartoon half body shot...: This describes the subject and content.//Replace background with...: This is a direct instruction.//pop art or comic book style, reminiscent of Roy Lichtenstein.: This is the style descriptor.The style descriptor is the most critical part for changing the final look.
You can modify the prompt by changing the style descriptor. Here are some examples:
//watercolor painting, soft brushstrokes, vibrant colors, impressionist style
//digital illustration, clean lines, vibrant colors, anime style
//photorealistic, high detail, 8k resolution, cinematic lighting
//surreal dreamlike, melting clocks, distorted perspective, ethereal atmosphere
You can describe different people or objects.
a cartoon half body shot of slender man to a cartoon half body shot of a beautiful woman.a cartoon half body shot of slender man to a cartoon full body shot of a majestic lion.You can describe different settings.
/the background is a photograph of a bustling city skyline at night
//filled with bright neon lights and towering skyscrapers.
Negative prompts are crucial for removing unwanted elements.
/blurry, low quality, distorted face
/deformed hands, extra fingers, malformed eyes
You can use parentheses to give more weight to certain words.
(pop art:1.3), comic book style
This tells the AI to pay 30% more attention to the “pop art” style.
(vibrant colors, bold lines, halftone dots)
By mastering prompt modification, you can unlock endless creative possibilities with ComfyUI.
Share